Toward Standardized Near-Data Processing with Unrestricted Data Placement for GPUs
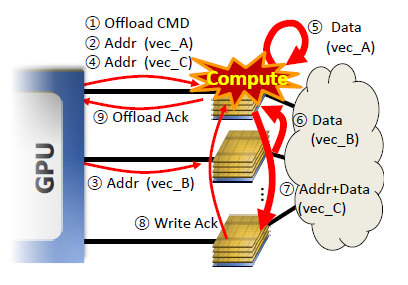
3D-stacked memory devices with processing logic can help alleviate the memory bandwidth bottleneck in GPUs. However, in order for such Near-Data Processing (NDP) memory stacks to be used for different GPU architectures, it is desirable to standardize the NDP architecture. Our proposal enables this standardization by allowing data to be spread across multiple memory stacks as is the norm in high-performance systems without an MMU on the NDP stack. The keys to this architecture are the ability to move data between memory stacks as required for computation, and a partitioned execution mechanism that offloads memory-intensive application segments onto the NDP stack and decouples address translation from DRAM accesses. By enhancing this system with a smart offload selection mechanism that is cognizant of the compute capability of the NDP and cache locality on the host processor, system performance and energy are improved by up to 66.8% and 37.6%, respectively.
Publication Date
Research Area
External Links
Uploaded Files
Copyright
Copyright by the Association for Computing Machinery, Inc. Permission to make digital or hard copies of part or all of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page. Copyrights for components of this work owned by others than ACM must be honored. Abstracting with credit is permitted. To copy otherwise, to republish, to post on servers, or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission and/or a fee. Request permissions from Publications Dept, ACM Inc., fax +1 (212) 869-0481, or permissions@acm.org. The definitive version of this paper can be found at ACM's Digital Library http://www.acm.org/dl/.
