Regularizing Neural Networks via Minimizing Hyperspherical Energy
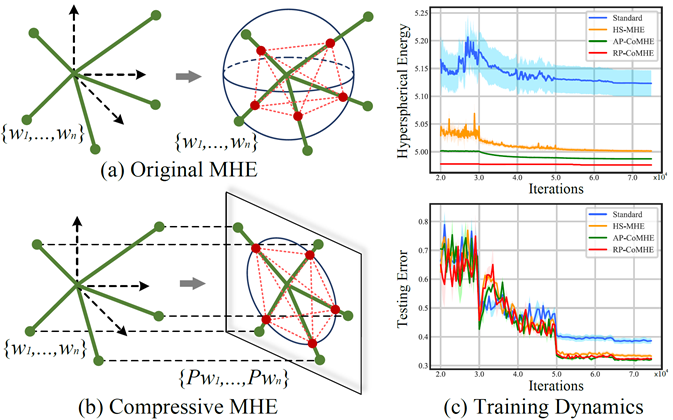
Inspired by the Thomson problem in physics where the distribution of multiple propelling electrons on a unit sphere can be modeled via minimizing some potential energy, hyperspherical energy minimization has demonstrated its potential in regularizing neural networks and improving their generalization power. In this paper, we first study the important role that hyperspherical energy plays in neural network training by analyzing its training dynamics. Then we show that naively minimizing hyperspherical energy suffers from some difficulties due to highly non-linear and non-convex optimization as the space dimensionality becomes higher, therefore limiting the potential to further improve the generalization. To address these problems, we propose the compressive minimum hyperspherical energy (CoMHE) as a more effective regularization for neural networks. Specifically, CoMHE utilizes projection mappings to reduce the dimensionality of neurons and minimizes their hyperspherical energy. According to different designs for the projection mapping, we propose several distinct yet well-performing variants and provide some theoretical guarantees to justify their effectiveness. Our experiments show that CoMHE consistently outperforms existing regularization methods, and can be easily applied to different neural networks.
Publication Date
Research Area
External Links
Copyright
This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Internal or personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution must be obtained from the IEEE by writing to pubs-permissions@ieee.org.
