Light-weight Head Pose Invariant Gaze Tracking
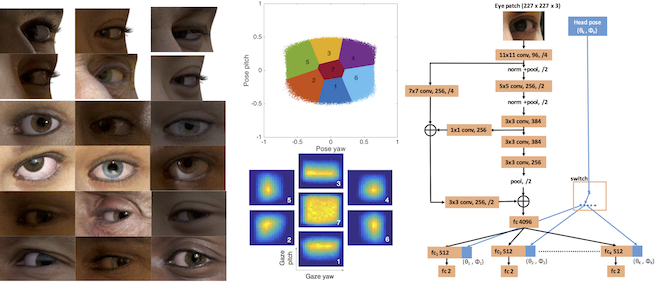
Unconstrained remote gaze tracking using off-the-shelf cameras is a challenging problem. Recently, promising algorithms for appearance-based gaze estimation using convolutional neural networks (CNN) have been proposed. Improving their robustness to various confounding factors including variable head pose, subject identity, illumination and image quality remain open problems. In this work, we study the effect of variable head pose on machine learning regressors trained to estimate gaze direction. We propose a novel branched CNN architecture that improves the robustness of gaze classifiers to variable head pose, without increasing computational cost. We also present various procedures to effectively train our gaze network including transfer learning from the more closely related task of object viewpoint estimation and from a large high-fidelity synthetic gaze dataset, which enable our ten times faster gaze network to achieve competitive accuracy to its current state-of-the-art direct competitor.
Publication Date
Uploaded Files
Award
Copyright
This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Internal or personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution must be obtained from the IEEE by writing to pubs-permissions@ieee.org.
