Learning Propagation for Arbitrarily-Structured Data
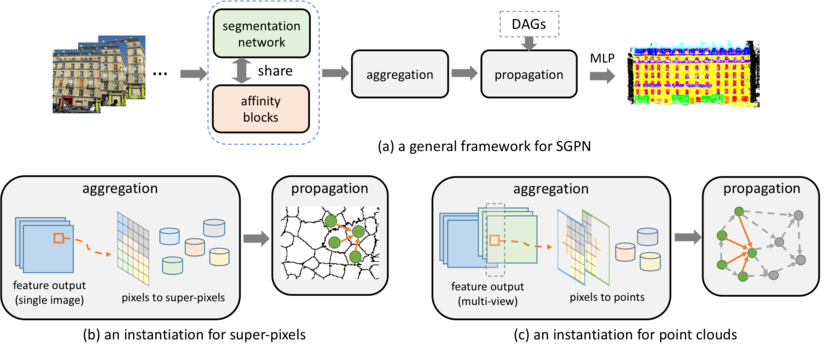
Processing an input signal that contains arbitrary structures, e.g., superpixels and point clouds, remains a big challenge in computer vision. Linear diffusion, an effective model for image processing, has been recently integrated with deep learning algorithms. In this paper, we propose to learn pairwise relations among data points in a global fashion to improve semantic segmentation with arbitrarily-structured data, through spatial generalized propagation networks (SGPN). The network propagates information on a group of graphs, which represent the arbitrarily-structured data, through a learned, linear diffusion process. The module is flexible to be embedded and jointly trained with many types of networks, e.g., CNNs. We experiment with semantic segmentation networks, where we use our propagation module to jointly train on different data -- images, superpixels, and point clouds. We show that SGPN consistently improves the performance of both pixel and point cloud segmentation, compared to networks that do not contain this module. Our method suggests an effective way to model the global pairwise relations for arbitrarily-structured data.
Publication Date
Research Area
External Links
Copyright
This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Internal or personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution must be obtained from the IEEE by writing to pubs-permissions@ieee.org.
