A Variable Warp Size Architecture
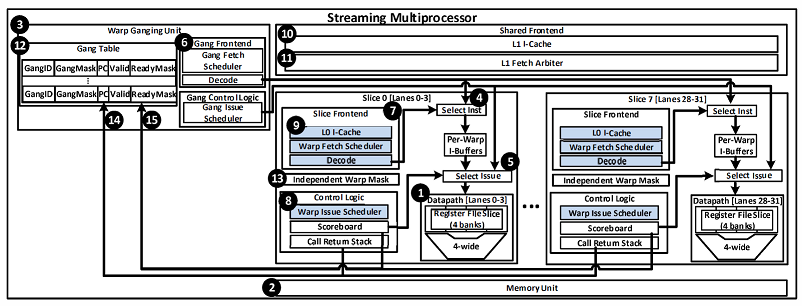
This paper studies the effect of warp sizing and scheduling on performance and efficiency in GPUs. We propose Variable Warp Sizing (VWS) which improves the performance of divergent applications by using a small base warp size in the presence of control flow and memory divergence. When appropriate, our proposed technique groups sets of these smaller warps together by ganging their execution in the warp scheduler, improving performance and energy efficiency for regular applications. Warp ganging is necessary to prevent performance degradation on regular workloads due to memory convergence slip, which results from the inability of smaller warps to exploit the same intra-warp memory locality as larger warps. This paper explores the effect of warp sizing on control flow divergence, memory divergence, and locality. For an estimated 5% area cost, our ganged scheduling microarchitecture results in a simulated 35% performance improvement on divergent workloads by allowing smaller groups of threads to proceed independently, and eliminates the performance degradation due to memory convergence slip that is observed when convergent applications are executed with smaller warp sizes.
Publication Date
Research Area
External Links
Uploaded Files
Copyright
Copyright by the Association for Computing Machinery, Inc. Permission to make digital or hard copies of part or all of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page. Copyrights for components of this work owned by others than ACM must be honored. Abstracting with credit is permitted. To copy otherwise, to republish, to post on servers, or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission and/or a fee. Request permissions from Publications Dept, ACM Inc., fax +1 (212) 869-0481, or permissions@acm.org. The definitive version of this paper can be found at ACM's Digital Library http://www.acm.org/dl/.
