Beyond Behavior Cloning in Autonomous Driving: a Survey of Closed-Loop Training Techniques
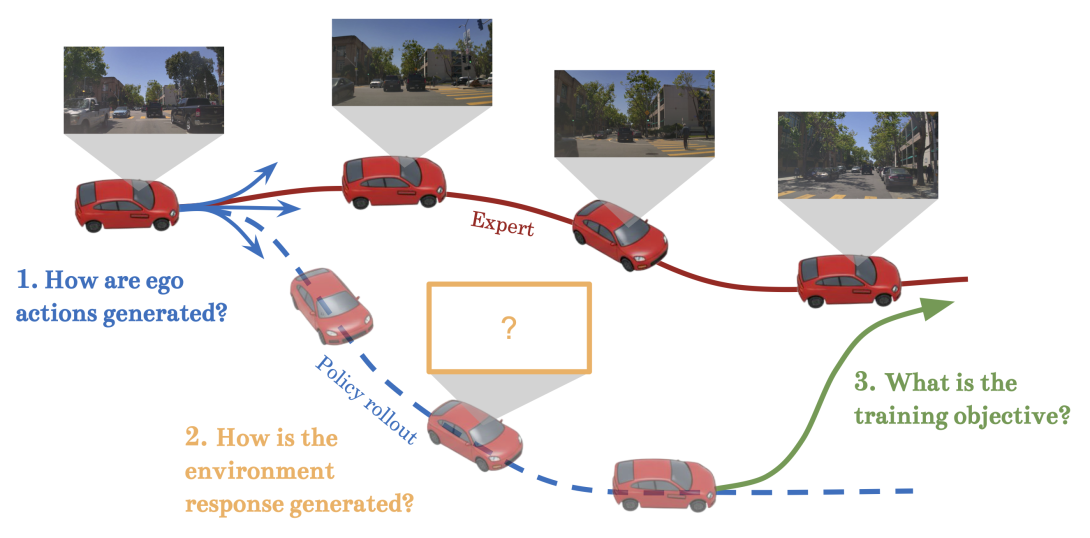
Behavior cloning, the dominant approach for training autonomous vehicle (AV) policies, suffers from a fundamental gap: policies trained open-loop on temporally independent samples must operate in closed-loop where actions influence future observations. This mismatch can cause covariate shift, compounding errors, and poor interactive behavior, among other issues. Closed-loop training mitigates the problem by exposing policies to the consequences of their actions during training. However, the recent shift to end-to-end ("sensor to action'') systems has made closed-loop training significantly more complex, requiring costly high-dimensional rendering and managing sim-to-real gaps. This survey presents a comprehensive taxonomy of closed-loop training techniques for end-to-end driving, organized along three axes: action generation (policy rollouts vs. perturbed demonstrations); environment response generation (real-world data collection, AV simulation, generative video and latent world models); and training objectives (closed-loop imitation, reinforcement learning, and their combinations). We analyze key trade-offs along each axis: on-policy vs. on-expert action generation, environment fidelity vs. cost, and expert vs. reward-based training objectives; as well as coupling factors, such as rollout deviation from the policy, expert, and real world logs; and data type, throughput, and latency requirements. The analysis reveals gaps between current research and industry practice, and points to promising directions for future work.
